In today’s digitally-driven world, the performance of your network is the backbone of your operations. Whether you’re setting up a home office, upgrading a small business, or architecting a large-scale data center, the choice of Ethernet cable is a foundational decision that impacts speed, reliability, and future scalability. Two of the most common and capable options on the market are Category 6 (Cat6) and Category 6A (Cat6A) cables.
As a leading manufacturer and supplier of high-performance cabling solutions, we at D-Lay Cable believe in empowering our clients with knowledge. Understanding the nuances between Cat6 and Cat6A is crucial for making a cost-effective and performance-oriented choice. dlaycable will break down their differences to help you select the perfect cable for your needs.
In This Article:
The Foundation: What is Cat6 Cable?
Category 6 (Cat6) cable was introduced as a significant improvement over its predecessor, Cat5e. It became the standard for many new installations due to its ability to handle higher speeds and its more robust construction against interference.
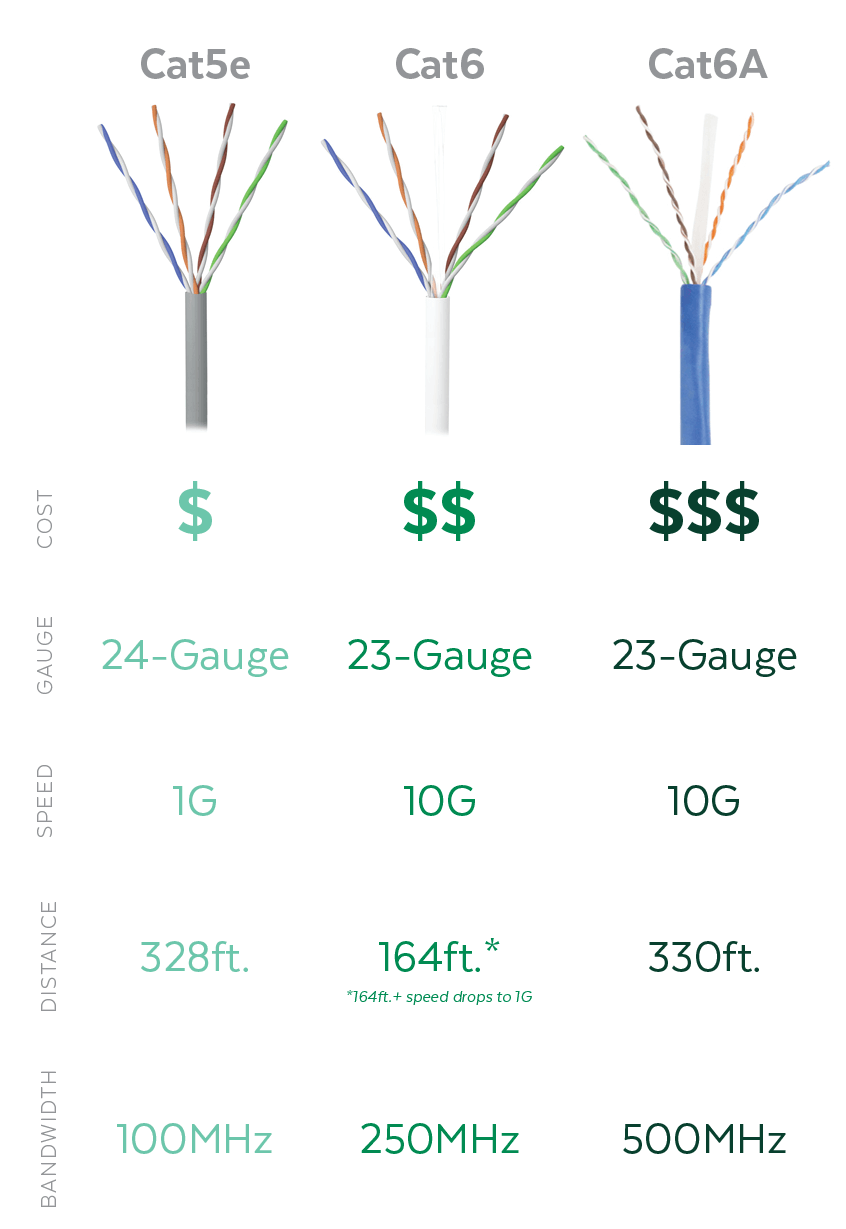
- Speed: It supports data rates of 1 Gbps up to 100 meters (328 feet). It can also support 10 Gbps speeds, but only over shorter distances, typically between 37-55 meters (121-180 feet), depending on the level of alien crosstalk in the environment.
- Bandwidth: Cat6 is rated for a frequency of 250 MHz. Think of bandwidth as the number of lanes on a highway; a higher MHz allows more data to travel simultaneously.
- Best For: Home networks, small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs), and applications where 1 Gbps is sufficient for the foreseeable future.
The Upgrade: What is Cat6A Cable?
Category 6A (Cat6A), with the “A” standing for “Augmented,” is the next evolution. It was specifically designed to reliably support the higher demands of 10 Gigabit Ethernet over the full distance of a standard channel.
- Speed: It consistently delivers 10 Gbps speeds over the full 100-meter (328 feet) distance. This makes it the default choice for networks requiring maximum performance.
- Bandwidth: Cat6A doubles the bandwidth of Cat6, operating at a frequency of 500 MHz. This wider “data highway” significantly reduces bottlenecks and improves overall performance.
- Best For: Data centers, large enterprises, healthcare facilities, smart buildings, and any new installation that needs to be “future-proofed” for the next decade of technological advancements.
Cat6 vs. Cat6A: A Head-to-Head Comparison
While speed and distance are the most cited differences, the engineering that enables these improvements is where the real distinction lies.
1. Performance: Bandwidth and 10Gbps Support
The most critical difference is how they handle 10 Gigabit Ethernet. While a high-quality Cat6 cable might achieve 10 Gbps in a perfect, short-distance scenario, Cat6A is guaranteed to deliver 10 Gbps over 100 meters. This reliability is due to its superior 500 MHz bandwidth, which provides more headroom for high-speed data transmission.
2. Crosstalk: The Battle Against Interference
Crosstalk is unwanted signal interference between adjacent cables. Cat6A is engineered to combat a specific, more troublesome type of interference called Alien Crosstalk (ANEXT). This is interference that “jumps” between cables in a bundle. Cat6A achieves this through:
- Thicker Conductors: It generally uses heavier 23 AWG copper conductors.
- Tighter Twists: The pairs of wires inside the cable are twisted more tightly.
- More Insulation: A thicker outer jacket and often additional internal elements (like a spline) physically separate the pairs and cables.
- Shielding (Optional but Common): Many Cat6A cables are shielded (F/UTP or S/FTP) to provide an additional barrier against all forms of electromagnetic interference (EMI), including ANEXT.
Cat6 has good protection against internal crosstalk but is far more susceptible to Alien Crosstalk, which is why its 10 Gbps performance degrades so quickly over distance.
3. Physical Construction and Installation
The enhancements that give Cat6A its superior performance also make it physically different. Cat6A cables are noticeably thicker, heavier, and less flexible than Cat6 cables. This has practical implications for installation:
- Bend Radius: Cat6A has a larger minimum bend radius, requiring more space for turns in conduits and pathways.
- Termination: Terminating the thicker conductors into jacks and patch panels requires more skill and often specific Cat6A-rated connectors.
- Cable Management: Its larger diameter means fewer cables can fit into a given conduit or cable tray.
4. Cost: The Budgetary Factor
There is a clear cost difference. Cat6A cables, connectors, and patch panels are more expensive than their Cat6 counterparts due to their more complex manufacturing and higher material content. However, this higher upfront cost can be a wise investment, potentially saving you from a costly network overhaul in the future.
Quick Comparison Table: Cat6 vs. Cat6A at a Glance
| Feature | Category 6 (Cat6) | Category 6A (Cat6A) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 10 Gbps (up to 55m) | 10 Gbps (up to 100m) |
| Bandwidth (Frequency) | 250 MHz | 500 MHz |
| Alien Crosstalk (ANEXT) | Susceptible | Significantly Reduced |
| Physical Size | Standard Thickness | Thicker and Heavier |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best Use Case | Home/SMB, 1Gbps Networks | Data Centers, Future-Proofing, 10Gbps Networks |
Making the Right Choice: Which Cable Do You Need?
Your decision should be based on your specific requirements for performance, environment, and budget.
Choose Cat6 if:
- Your network traffic primarily consists of standard office tasks, web browsing, and streaming.
- Your network devices and internet connection are 1 Gbps or less.
- The budget is a primary constraint.
- You are upgrading an existing, less demanding environment like a home or small office.
Choose Cat6A if:
- You are planning a new construction or major renovation. The marginal cost increase is minimal compared to the cost of future replacement.
- Your network must support 10 Gbps speeds now or in the near future.
- The installation is for a data center, hospital, university, or large corporate office.
- You are deploying high-power Power over Ethernet (PoE++) devices, as Cat6A’s thicker conductors handle heat better.
- You need to ensure maximum performance and future-proof your infrastructure against emerging technologies.
Conclusion: Partner with D-Lay Cable for Quality and Performance
The choice between Cat6 and Cat6A is a choice between meeting today’s standards and investing in tomorrow’s. While Cat6 remains a viable and cost-effective solution for many applications, Cat6A is the clear winner for performance, reliability, and long-term value.
At D-Lay Cable, we manufacture and supply a comprehensive range of both Cat6 and Cat6A cables, available in UTP (Unshielded) and various shielded configurations to meet the specific demands of your environment. All our products are rigorously tested to exceed industry standards and come with certifications like UL, ETL, and RoHS, ensuring you receive a product you can trust.
With our commitment to quality, competitive pricing, fast delivery, and extensive OEM/ODM customization capabilities, we are your ideal partner for building a robust and future-ready network. Explore our website or contact our expert team today to find the perfect cabling solution for your project.

