The primary difference between Cat 7 and Cat 8 cables lies in their transmission speed and frequency bandwidth. Cat 7 offers a maximum speed of 10 Gbps with a bandwidth of 600 MHz over 100 meters, making it suitable for smart homes and enterprise networks. In contrast, Cat 8 is the latest IEEE standard designed for data centers, capable of speeds up to 40 Gbps with a massive bandwidth of 2000 MHz (2 GHz), though its maximum speed is limited to a distance of 30 meters. While Cat 7 serves as a robust shield against interference, Cat 8 provides cutting-edge performance for future-proofing high-density network environments.
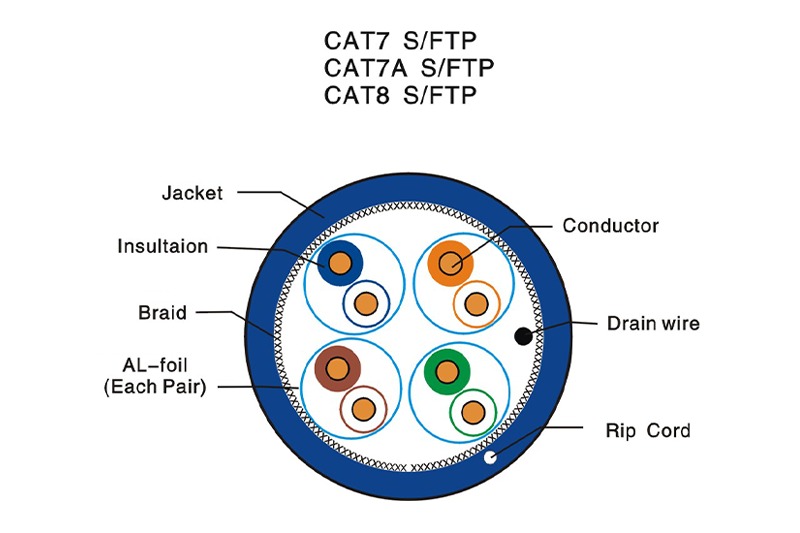
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Modern Ethernet Standards
- What is Cat 7 Cable? Specs and Reality
- What is Cat 8 Cable? The New Speed King
- Cat 7 vs Cat 8: The Head-to-Head Comparison
- Connector Compatibility: RJ45 vs. TERA/GG45
- Real-World Scenarios: Gaming, Home, and Data Centers
- Final Verdict: Which Cable Should You Choose?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to Modern Ethernet Standards
In the evolving landscape of network infrastructure, selecting the right cabling is pivotal for ensuring data integrity and speed. While wireless technology has advanced, physical cabling remains the gold standard for stability, low latency, and security. For years, Cat 5e and Cat 6 were the household staples, but as file sizes grow and 4K/8K streaming becomes the norm, the demand for higher bandwidth has pushed users toward Cat 7 and Cat 8 ethernet cables. Understanding the nuances between these two categories is essential for avoiding unnecessary expenses while ensuring your network is future-proof.
What is Cat 7 Cable? Specs and Reality
Category 7, or Cat 7, was introduced to satisfy the demands of 10 Gigabit Ethernet over 100 meters of copper cabling. It is characterized by a frequency of 600 MHz. One of the defining features of Cat 7 is its strict specifications regarding crosstalk and system noise. To achieve this, Cat 7 utilizes S/FTP (Screened Foiled Twisted Pair) or F/FTP shielding. essentially, individual pairs are shielded, and an overall screen covers the bundle. This makes the cable thicker and stiffer than its predecessors but virtually immune to alien crosstalk.
However, there is a caveat regarding Cat 7 that often confuses consumers. Cat 7 is an ISO/IEC 11801 standard, but it is not officially recognized by the TIA/EIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) in the United States. Consequently, many equipment manufacturers skipped over Cat 7 development in favor of Cat 6A or jumped straight to Cat 8. Despite this, Cat 7 remains a popular choice in the European market and among enthusiasts who want better shielding than Cat 6A provides.
What is Cat 8 Cable? The New Speed King
Category 8, or Cat 8, is the latest copper Ethernet cable officially recognized by the TIA/EIA under the ANSI/TIA-568-C.2-1 standard. It represents a massive leap in performance, designed specifically to support 25GBASE-T and 40GBASE-T (25 and 40 Gigabit Ethernet). Cat 8 operates at a frequency of 2000 MHz (2 GHz), which is more than three times the bandwidth of Cat 7.
The architecture of Cat 8 is heavily shielded, similar to Cat 7, to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI). However, the trade-off for this extreme speed is distance. While Cat 7 maintains its top speed over 100 meters, Cat 8 is limited to a 30-meter reach (approximately 98 feet) for 40 Gbps speeds. This limitation positions Cat 8 primarily as a solution for data centers (connecting switches to servers) rather than for long-distance structural cabling in an office building or large home.
Cat 7 vs Cat 8: The Head-to-Head Comparison
To fully grasp the difference, we must look at the technical specifications side-by-side. The following table illustrates the performance gap between these two high-end cables.
| Feature | Cat 7 Cable | Cat 8 Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed (Throughput) | 10 Gbps | 25 Gbps / 40 Gbps |
| Frequency (Bandwidth) | 600 MHz | 2000 MHz (2 GHz) |
| Max Distance @ Max Speed | 100 Meters | 30 Meters |
| Shielding Type | S/FTP (Heavy Shielding) | S/FTP (Heaviest Shielding) |
| TIA/EIA Recognized? | No (ISO/IEC Standard) | Yes |
| Flexibility | Rigid/Stiff | Very Rigid/Thick |
Speed and Frequency
The most distinct difference is the frequency. Is Cat 8 faster than Cat 7? Yes, significantly. The 2000 MHz bandwidth of Cat 8 allows for faster data transfer rates, reducing latency and increasing throughput. However, for a standard home internet connection (usually 1 Gbps or rarely 2-5 Gbps), both cables are technically overkill, though Cat 8 offers a higher ceiling for local file transfers, such as moving large video files to a NAS (Network Attached Storage) server.
Shielding and EMI
Both cables excel in shielding. They use twisted pairs wrapped in foil, encased in an outer braid. This construction eliminates crosstalk (signal bleeding between wires) and protects against EMI (Electromagnetic Interference). If you are running cables near high-voltage electrical wiring or in an industrial setting, both Cat 7 and Cat 8 will perform better than unshielded Cat 5e or Cat 6.
Connector Compatibility: RJ45 vs. TERA/GG45
This is a critical, often overlooked technical detail. Cat 8 cables universally use the standard RJ45 connector, making them backward compatible with almost every router, switch, Playstation, Xbox, and PC on the market today. You can plug a Cat 8 cable into a 10-year-old router, and it will work immediately (at the router’s speed).
Cat 7 is more complicated. While many consumer-grade “Cat 7” cables sold on marketplaces like Amazon come with RJ45 plugs, true industrial Cat 7 standards often utilize non-RJ45 connectors like the GG45 (GigaGate 45) or TERA connectors to maximize the 600 MHz potential. Using a standard RJ45 on a Cat 7 cable can technically degrade its performance slightly, bringing it closer to Cat 6A standards. However, for consumer applications, the “Cat 7 with RJ45” patch cables are generally sufficient and widely compatible.
Real-World Scenarios: Gaming, Home, and Data Centers
Is Cat 8 better for Gaming?
Gamers constantly ask: “Will Cat 8 improve my ping?” The honest answer is: likely not noticeably compared to Cat 7 or even Cat 6A. Latency in gaming is primarily dictated by your ISP and the distance to the game server. However, Cat 8’s superior shielding can prevent packet loss caused by interference, providing a marginally more stable connection in electronically noisy environments (like a dorm room filled with devices).
Home Network and Smart Home
For a typical smart home, Cat 7 is often seen as a “sweet spot” for enthusiasts. It offers 10 Gigabit speeds which are future-proof for the next decade of home internet evolution. However, because Cat 8 has become more affordable, many users are buying Cat 8 for short patch leads (e.g., from the modem to the router) simply to ensure zero bottlenecks at the source.
Data Centers and Server Rooms
This is where Cat 8 shines. In a Top-of-Rack (ToR) or End-of-Row (EoR) topology where switches are within 30 meters of the servers, Cat 8 is the cost-effective alternative to fiber optics. It allows data centers to push 40 Gbps over copper without the expensive transceivers required for fiber connections.
Final Verdict: Which Cable Should You Choose?
Choosing between Cat 7 and Cat 8 depends entirely on your specific use case, budget, and required cable length.
- Choose Cat 7 if: You need to run cables through walls over long distances (up to 100m) and require 10 Gbps speeds. It is generally cheaper than Cat 8 and offers excellent shielding. However, be aware that Cat 6A can usually do the same job for less money.
- Choose Cat 8 if: You need the absolute highest performance for short distances (under 30m). It is ideal for connecting a high-speed NAS, a high-end gaming PC to a nearby switch, or for future-proofing a professional home lab. Since it is TIA/EIA recognized, it is a more “official” standard than Cat 7.
- Stick to Cat 6A if: You are a standard home user. Cat 6A supports 10 Gbps and is easier to install (more flexible) than both Cat 7 and Cat 8.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I use Cat 8 cable with a standard router?
A: Yes, Cat 8 is fully backward compatible. It works with any device that accepts an RJ45 connector, including older routers, switches, and computers.
Q: Is Cat 7 obsolete?
A: Not technically, but it occupies an awkward position. Since Cat 6A handles 10Gbps and Cat 8 handles 40Gbps, Cat 7 is often skipped by professional installers in favor of Cat 6A or Fiber.
Q: Why is Cat 8 cable so thick?
A: The thickness comes from the heavy shielding (S/FTP) required to support 2000 MHz frequencies without signal degradation or interference.

