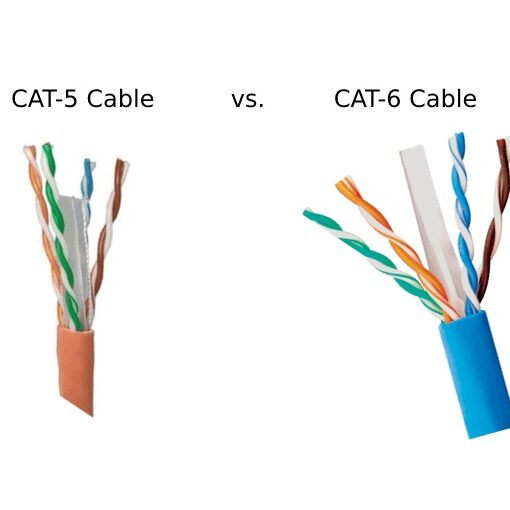
The main difference between CAT5e and CAT6 cables lies in performance and bandwidth. CAT6 cables support data transfer speeds up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps) and a bandwidth of 250 MHz, while CAT5e supports up to 1 Gbps at 100 MHz bandwidth. This means CAT6 can handle more data simultaneously and is better shielded against interference, making it a more robust and future-proof option for demanding applications like gaming, 4K streaming, and busy office networks. However, for most standard home internet connections up to 1 Gbps, CAT5e remains a perfectly capable and more budget-friendly choice.
Table of Contents
- At a Glance: The Key Differences Between CAT5e and CAT6
- What is CAT5e Cable? The Reliable Workhorse
- What is CAT6 Cable? The Performance Upgrade
- The Nitty-Gritty: A Deep Dive into Technical Specs
- Real-World Scenarios: Which Cable Should You Choose?
- Common Questions and Misconceptions (FAQ)
- The Final Verdict: Making the Right Choice for Your Network
At a Glance: The Key Differences Between CAT5e and CAT6
When you’re standing in an electronics aisle or browsing online, the jargon can be overwhelming. Let’s cut through the noise with a straightforward comparison. While both cables use the same RJ-45 connector and plug into the same Ethernet ports, their internal construction and capabilities are what set them apart.
| Specification | CAT5e (Category 5 Enhanced) | CAT6 (Category 6) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 1 Gbps @ 100 meters | 10 Gbps @ up to 55 meters; 1 Gbps @ 100 meters |
| Max Bandwidth (Frequency) | 100 MHz | 250 MHz |
| Crosstalk Reduction | Standard twisted pairs | Tighter twisted pairs, often with a spline (plastic separator) |
| Cost | Lower | Slightly Higher (approx. 20-30% more) |
| Best For | Home networks with internet speeds up to 1 Gbps, basic office use. | High-demand networks, gaming, 4K/8K streaming, future-proofing. |
What is CAT5e Cable? The Reliable Workhorse
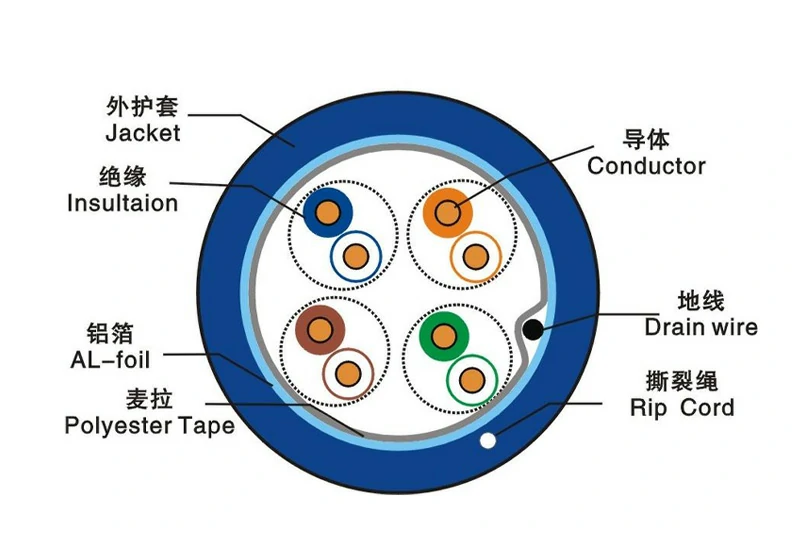
Think of CAT5e (Category 5 Enhanced) as the long-standing champion of home and office networking. Introduced in 2001, it was a significant upgrade over the original CAT5 standard, offering better performance and reduced interference. For nearly two decades, it has been the go-to cable for connecting computers, routers, and other network devices.
Performance and Capabilities
CAT5e is designed to reliably support speeds up to 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps) over a maximum distance of 100 meters (328 feet). It operates at a frequency, or bandwidth, of 100 MHz. This is more than enough for the vast majority of current home internet plans, which typically top out at 1 Gbps. It can handle everyday tasks like web browsing, HD video streaming, and online document collaboration without breaking a sweat.
Common Use Cases for CAT5e
This cable is the perfect economical choice for scenarios where you don’t need to push the absolute limits of networking technology. It excels in environments such as a standard home network for connecting your PC to a router, hooking up a smart TV for streaming Netflix in HD, or wiring a small office for basic internet access and file sharing. If your internet speed is 1 Gbps or less, CAT5e will serve you well.
Pros and Cons of Sticking with CAT5e
The biggest advantage of CAT5e is its cost-effectiveness and flexibility. The cables are thinner and easier to route around corners and through walls. For existing networks with gigabit switches and routers, it provides all the performance you need at a lower price point. The main drawback is its lack of future-proofing. As internet speeds continue to increase beyond 1 Gbps and local network demands grow, CAT5e will become a bottleneck.
What is CAT6 Cable? The Performance Upgrade
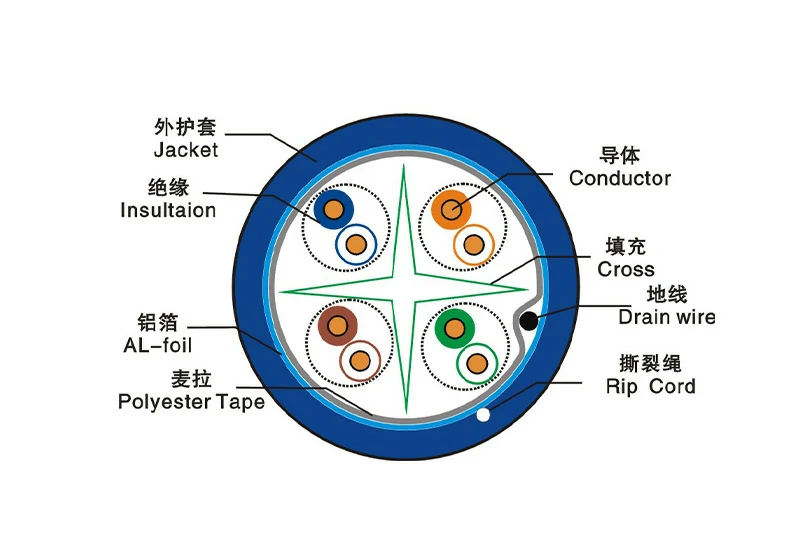
CAT6 (Category 6) is the next evolution in Ethernet cabling, engineered specifically for higher performance and a more stable connection in noisy environments. It represents a significant step up in capability, designed to meet the demands of modern and future high-speed networks.
How CAT6 Achieves Higher Performance
While CAT6 also supports 1 Gbps speeds over the full 100-meter distance, its true advantage is the ability to handle up to 10 Gbps at shorter distances (typically up to 55 meters or 180 feet). More importantly, it boasts a bandwidth of 250 MHz—two and a half times that of CAT5e. This wider “highway” for data allows more information to travel simultaneously, which is crucial for high-traffic networks where multiple devices are streaming, downloading, and gaming at once.
The Physical Difference: Tighter Twists and Splines
So, how does CAT6 achieve this superior performance? It comes down to its physical construction. CAT6 cables feature more tightly twisted pairs of copper wires than CAT5e. This tighter twist rate is a primary defense against electronic interference and crosstalk. Many CAT6 cables also include a plastic separator, known as a spline, that runs down the center of the cable, physically isolating each of the four wire pairs from the others. This further reduces internal signal interference, leading to a cleaner, more reliable data transmission.
Common Use Cases for CAT6
CAT6 is the cable of choice for anyone who wants to maximize their network’s performance and prepare for the future. It’s ideal for competitive online gamers seeking the lowest possible latency, content creators transferring massive video files across a local network, and households running multiple 4K or 8K video streams. It’s also the standard recommendation for any new in-wall wiring installations to ensure the home is ready for next-generation multi-gig internet speeds.
The Nitty-Gritty: A Deep Dive into Technical Specs
Understanding the numbers on the box helps in making an informed decision. Let’s break down the most critical specifications—speed, bandwidth, and crosstalk—and what they mean for your actual experience.
Speed vs. Bandwidth: What’s More Important?
It’s easy to confuse speed (measured in Gbps) and bandwidth (measured in MHz), but they describe different things.
- Speed is how fast data can travel down the cable. Think of it as the speed limit on a highway.
- Bandwidth is the capacity of the cable to handle traffic. Think of it as the number of lanes on that highway.
A CAT5e cable (100 MHz) is like a two-lane highway with a 65 MPH speed limit. A CAT6 cable (250 MHz) is like a five-lane highway with the same 65 MPH speed limit (for 1 Gbps). While both can get a car from A to B at the same speed, the CAT6 highway can handle far more cars at once without causing a traffic jam. This is why CAT6 is better for environments with many connected devices all demanding data.
Why Crosstalk Matters (And How CAT6 Reduces It)
Crosstalk is the “signal bleed” or interference that occurs between adjacent wire pairs inside a cable. Too much crosstalk can lead to data errors, packet loss, and reduced network performance. It’s like trying to have a conversation in a crowded room where you can hear snippets of other conversations. CAT6’s stricter construction standards, including tighter twists and the optional spline, are specifically designed to minimize this crosstalk, ensuring a more stable and error-free signal than CAT5e.
Understanding Cable Length Limitations
For both CAT5e and CAT6, the maximum recommended length for achieving a guaranteed 1 Gbps speed is 100 meters (328 feet). This includes the total length of the cable run, including patch panels and wall jacks. However, the 10 Gbps speed of a CAT6 cable is only officially supported up to 55 meters. Beyond that distance, its performance will drop back down to 1 Gbps. For most home and small office applications, this length limitation is rarely an issue.
Real-World Scenarios: Which Cable Should You Choose?
Technical specs are great, but the best choice depends entirely on you. Let’s apply this knowledge to some common situations.
For the Average Home User
If your internet plan is 1 Gbps or less, and your primary activities are web browsing, social media, and streaming HD video on one or two devices, CAT5e is perfectly adequate and will save you money. Your internet connection will be the bottleneck long before your cable is. There’s no performance benefit to using a CAT6 cable if the rest of your network hardware and internet plan don’t support speeds over 1 Gbps.
For Gamers and Power Users
If you’re a competitive online gamer, a streamer, or someone who regularly transfers large files between computers on your home network (like from a PC to a NAS), CAT6 is the clear winner. The superior crosstalk reduction provides a more stable connection, which can lead to lower ping times and a smoother gaming experience. The higher bandwidth is also beneficial when your network is under heavy load from multiple sources.
For Small Businesses and Offices
For any new business installation or office network setup, investing in CAT6 (or even CAT6a) is the wisest decision. Office environments typically have higher network traffic, more devices, and a greater potential for electromagnetic interference. The reliability and higher performance of CAT6 will ensure smooth operations for years to come and support future technologies like multi-gig speeds and advanced VoIP systems.
The “Future-Proofing” Argument: Is It Worth It?
If you are running new cables through your walls, the small additional cost of CAT6 is absolutely worth it. The labor to install cables is the most expensive part of the job, so choosing the better cable now saves you from a costly upgrade later. With internet service providers beginning to roll out 2 Gbps, 5 Gbps, and even 10 Gbps residential plans, a CAT6 infrastructure ensures you’ll be ready to take full advantage of them.
Common Questions and Misconceptions (FAQ)
Will CAT6 make my internet connection faster?
No, not directly. Your Ethernet cable cannot make your internet faster than the plan you pay for from your Internet Service Provider (ISP). If you pay for a 500 Mbps plan, a CAT6 cable will still only deliver 500 Mbps from the internet. However, a high-quality CAT6 cable can ensure you are getting the full speed you pay for with maximum stability, and it can speed up data transfers within your local network.
Are CAT5e and CAT6 cables and connectors interchangeable?
Yes, they are fully backward compatible. Both standards use the same RJ-45 connector. You can plug a CAT6 cable into a device with a CAT5e port, or a CAT5e cable into a CAT6 port. The network will simply operate at the speed of the slowest component in the chain. To get the full benefit of CAT6, your router, switch, and device must all have ports that support the desired speed (e.g., 10 Gbps).
What about CAT6a, CAT7, and CAT8?
These are even higher-performance standards:
- CAT6a (Augmented): Supports 10 Gbps speeds over the full 100-meter distance and has a bandwidth of 500 MHz. It’s the standard for 10 Gbps business networks.
- CAT7/CAT8: These are heavily shielded, high-frequency cables designed primarily for data center and enterprise environments. They are overkill and often impractical for residential use due to their stiffness and proprietary connector requirements (in the case of CAT7).
For most users, the choice remains firmly between CAT5e and CAT6.
Does the quality of the cable matter?
Absolutely. Regardless of category, always choose cables with 100% pure copper conductors. Avoid cheaper Copper Clad Aluminum (CCA) cables. CCA cables are brittle, have higher signal loss, and are not compliant with TIA standards for Ethernet wiring. Also, consider if you need a Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cable for environments with high electronic interference (like near power lines or large motors) versus the more common Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP).
The Final Verdict: Making the Right Choice for Your Network
The debate between CAT5e and CAT6 isn’t about which one is “best,” but which one is best for you. The decision boils down to a simple trade-off between current needs, future goals, and budget.
Choose CAT5e if:
- Your internet speed is 1 Gbps or less.
- You are on a tight budget.
- Your primary use is general web browsing and HD streaming.
- You are simply replacing a short, visible patch cable.
Choose CAT6 if:
- You are installing new cables inside walls or in hard-to-reach places.
- You are a competitive gamer, a content creator, or a power user.
- Your home or office has many devices competing for network bandwidth.
- You want to ensure your network is ready for multi-gig internet speeds in the future.
For a minimal price increase, CAT6 provides a more stable, capable, and future-ready foundation for your network. While CAT5e is still a reliable workhorse, the performance and peace of mind offered by CAT6 make it the recommended choice for most new purchases and all new installations.