CAT6A bulk cables with robust M12 connectors and shielding deliver 10Gbps speeds for industrial automation, ensuring reliable data transfer in harsh environments.
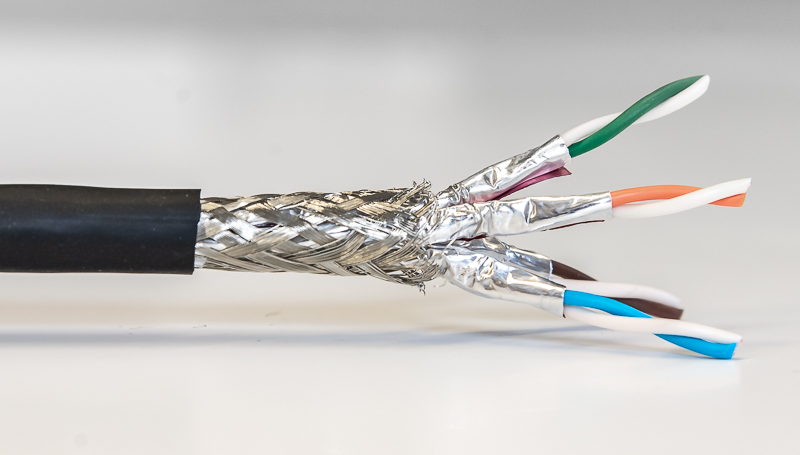
Table of Contents
- Why is CAT6A Essential for Modern Industrial Automation?
- The Critical Role of M12 Connectors in Harsh Environments
- How Robust Shielding Protects Data Integrity
- Key Construction Elements of High-Performance Industrial CAT6A Cable
- Selecting the Right CAT6A Bulk Cable for Your Application
- Frequently Asked Questions about Industrial CAT6A Cables
Why is CAT6A Essential for Modern Industrial Automation?
The evolution of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has transformed factory floors into highly connected, data-driven ecosystems. This shift demands a network infrastructure capable of handling massive data throughput with uncompromising reliability. Category 6A (CAT6A) Ethernet cabling emerges as the benchmark standard, engineered to support the demanding speeds and bandwidth required by advanced automation systems. Its ability to deliver 10 Gbps data rates over distances up to 100 meters provides the necessary performance for high-resolution machine vision, real-time sensor data processing, and complex robotic controls.
Beyond raw speed, CAT6A operates at a bandwidth of 500 MHz, double that of its predecessor, CAT6. This increased bandwidth reduces the potential for data bottlenecks and ensures consistent performance as more devices are added to the network. By implementing CAT6A infrastructure, manufacturers are not just meeting current needs; they are future-proofing their operations. This foresight allows for seamless integration of next-generation technologies without requiring a complete overhaul of the physical network layer, ensuring a scalable and cost-effective path for growth.
The Critical Role of M12 Connectors in Harsh Environments
In industrial settings, standard office-grade connectors like the RJ45 are a significant point of failure. They are susceptible to vibration, moisture, dust, and chemical exposure, all of which are common on a factory floor. This is where the M12 connector demonstrates its superiority. Its robust, circular design with a threaded coupling mechanism ensures a secure, locked connection that resists vibration and mechanical shock. This prevents intermittent data loss and network downtime, which can halt production lines and cause significant financial losses.
Furthermore, M12 connectors are designed with ingress protection in mind, typically carrying an IP67 or higher rating. This means they are completely sealed against dust and can withstand temporary immersion in water. This level of protection is indispensable for applications in washdown areas, food and beverage processing, and outdoor installations where environmental hazards are a constant. The combination of a secure physical lock and environmental sealing makes the M12 connector the definitive choice for maintaining network integrity in challenging industrial conditions.
Comparing M12 and RJ45 Connectors
To understand the practical advantages of M12 connectors for industrial applications, a direct comparison with the common RJ45 connector is helpful. While RJ45 connectors are ubiquitous in commercial and office environments, their design limitations become apparent when subjected to industrial stress.
| Feature | M12 Connector | RJ45 Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Style | Threaded, locking circular design | Plastic latching tab |
| Vibration Resistance | Excellent; designed to resist shock and vibration | Poor; latch can break and connection can loosen |
| Ingress Protection (IP) Rating | Typically IP67, IP68, IP69K (dust-tight and waterproof) | Typically IP20 (no protection from liquids or dust) |
| Ideal Environment | Industrial, factory floor, outdoor, washdown | Office, data center, clean commercial spaces |
| Durability | High; often features metal housing | Low; typically all-plastic construction |
Understanding M12 Coding for Ethernet Applications
M12 connectors are not a one-size-fits-all solution; they use different “keying” or “coding” patterns to prevent incorrect mating of cables for different applications (e.g., power, sensor, networking). For industrial Ethernet, two codes are primary: D-code and X-code. D-coded M12 connectors feature 4 pins and are suitable for 10/100 Mbps Ethernet (CAT5/CAT5e). While functional for many legacy systems, they do not support the higher speeds of modern networks.
For CAT6A and its 10 Gbps capabilities, the X-coded M12 connector is the required standard. It features 8 pins with pairs separated by a cross-shaped shield (the “X”). This design provides superior crosstalk isolation between the twisted pairs, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity at the high frequencies used by 10 Gigabit Ethernet. When specifying a CAT6A network for an industrial setting, ensuring the use of X-coded M12 connectors is crucial for unlocking the full performance of the cable.
How Robust Shielding Protects Data Integrity
Industrial environments are electrically noisy. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), servo motors, welding equipment, and large power lines all generate significant Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI). When this electrical noise corrupts the data signals traveling through an Ethernet cable, it can lead to packet loss, reduced speeds, and even complete communication failure. This is why robust shielding is not an option but a necessity for industrial CAT6A cables.
Shielding acts as a Faraday cage around the core conductors, intercepting stray electrical noise and safely directing it to the ground. This protects the delicate data signals from corruption, ensuring clean, error-free transmission. A properly shielded cable system provides a stable and reliable network foundation, which is paramount for processes that depend on precise timing and data accuracy, such as synchronized robotic arms or real-time quality control imaging.
Types of Shielding in Industrial CAT6A Cables
Industrial CAT6A cables employ sophisticated, multi-layer shielding to provide maximum protection. The most common and effective type for industrial use is S/FTP (Screened/Foiled Twisted Pair). In this construction, each of the four twisted pairs is individually wrapped in a foil shield (FTP) to prevent crosstalk between them. An overall braided screen (S) is then wrapped around all four pairs to provide comprehensive protection from external EMI/RFI. This dual-layer approach offers superior noise immunity compared to simpler shielding methods like F/UTP (overall foil shield) or U/FTP (individual pair foils only).
At D-Lay Cable, we engineer our industrial CAT6A cables with robust S/FTP shielding using high-coverage braids and durable foil layers. This ensures our cables meet and exceed the stringent requirements for noise immunity in the most demanding factory environments, guaranteeing the integrity of your critical data streams.
The Impact of EMI/RFI on Factory Operations
The consequences of data corruption from EMI/RFI extend beyond slow network speeds. In an automated system, a lost data packet could mean a robot misses a command, a safety sensor fails to report an obstacle, or a quality control camera transmits a flawed image. These failures can lead to production errors, equipment damage, costly downtime, and potential safety hazards. By investing in properly shielded industrial-grade CAT6A cables, facilities protect their entire operational workflow, ensuring that control signals and critical data arrive intact and on time.
Key Construction Elements of High-Performance Industrial CAT6A Cable
The performance of an industrial CAT6A cable is determined by more than just its shielding and connector. The core construction materials play a vital role in its durability and longevity. High-performance cables typically use stranded pure copper conductors, which offer excellent flexibility for applications involving repeated motion, such as on a robotic arm or moving gantry. This is a marked improvement over solid conductors, which are rigid and can break after repeated flexing.
The outer jacket is the cable’s first line of defense. While standard commercial cables use PVC, industrial cables require more resilient compounds. Polyurethane (PUR) is a premium choice, offering exceptional resistance to industrial oils, chemicals, and abrasion. It also remains flexible in a wide range of temperatures. Another robust option is Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE), known for its extreme flexibility and durability in continuous motion applications. The choice of jacket material directly impacts the cable’s lifespan and suitability for specific environmental challenges.
Selecting the Right CAT6A Bulk Cable for Your Application
Choosing the correct industrial CAT6A bulk cable involves a systematic evaluation of the intended operational environment and mechanical demands. A one-size-fits-all approach can lead to premature cable failure and network instability. A thorough assessment ensures that the selected cable provides a reliable, long-term solution.
Environmental Factors to Consider
Begin by analyzing the environment where the cable will be installed. What is the ambient operating temperature range? Will the cable be exposed to direct sunlight (UV radiation), which can degrade certain jacket materials? Is there contact with oils, solvents, or other corrosive chemicals? Will the cable be used in a washdown area requiring resistance to high-pressure water jets? Answering these questions will guide the selection of the appropriate jacket material (e.g., PUR for oil resistance) and help determine if a specific IP rating is necessary for connected components.
Mechanical Stress and Motion Requirements
Next, consider the physical stresses the cable will endure. Is the application stationary, or will the cable be in constant motion? For robotics, cable tracks, and other dynamic systems, a high-flex rated cable is essential. These cables are designed with specialized conductors, insulation, and fillers to withstand millions of flex cycles without conductor breakage. Also, assess the potential for torsional (twisting) stress or abrasion from dragging. Specifying a cable with the correct flex rating and a durable, abrasion-resistant jacket is critical for mechanical reliability.
Network Protocol and Bandwidth Needs
Finally, confirm that the cable’s performance characteristics align with your network protocol and future goals. While CAT6A is designed for 10 Gbps, it is also fully backward compatible with slower protocols like EtherNet/IP, PROFINET, and Modbus TCP. Selecting CAT6A provides the headroom to upgrade network hardware and accommodate data-intensive applications in the future without the need to replace the physical cabling infrastructure. This strategic choice ensures your network can scale with your operational demands.
Frequently Asked Questions about Industrial CAT6A Cables
What is the maximum length for an industrial CAT6A run?
The TIA/EIA standard specifies a maximum channel length of 100 meters (328 feet) for CAT6A cable to achieve its full 10 Gbps performance. This length includes the total run of bulk cable plus patch cords at both ends. In electrically noisy industrial environments, it is best practice to respect this limit to ensure reliable signal integrity.
Can I use commercial-grade CAT6A cable in a factory?
It is strongly discouraged. Commercial-grade cables lack the robust jacket materials, heavy-duty shielding, and vibration-resistant connectors (like M12) needed to withstand industrial hazards. Using them can lead to frequent network failures, data loss, and a significantly shorter service life, ultimately costing more in downtime and replacement.
Are M12 connectors difficult to terminate in the field?
While M12 connectors require more steps to terminate than a simple RJ45 crimp, field-terminable versions are widely available. These connectors often use screw-terminals or insulation-displacement contacts (IDC) that do not require specialized crimping tools, allowing technicians to create custom-length cables on-site with reliable, IP-rated connections.

